Ir Emittance Roof
Determining the thermal emittance and solar reflectance of building materials especially roofing materials can be very useful for reducing heating and cooling energy costs in buildings.
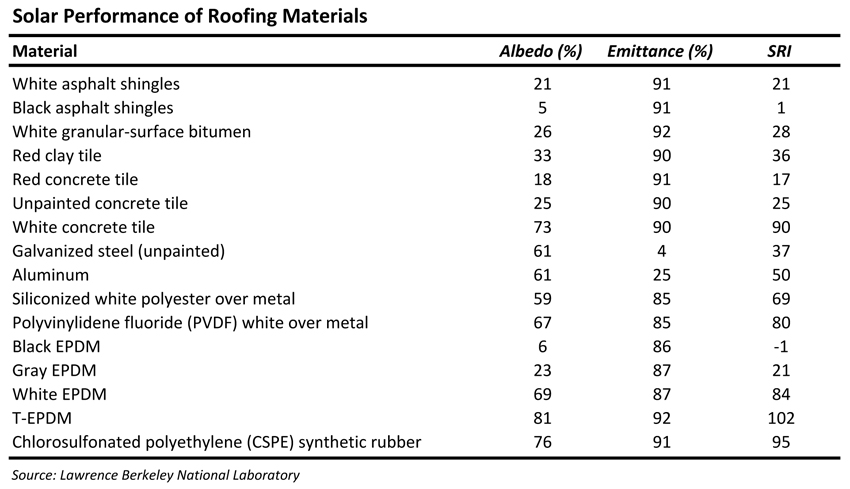
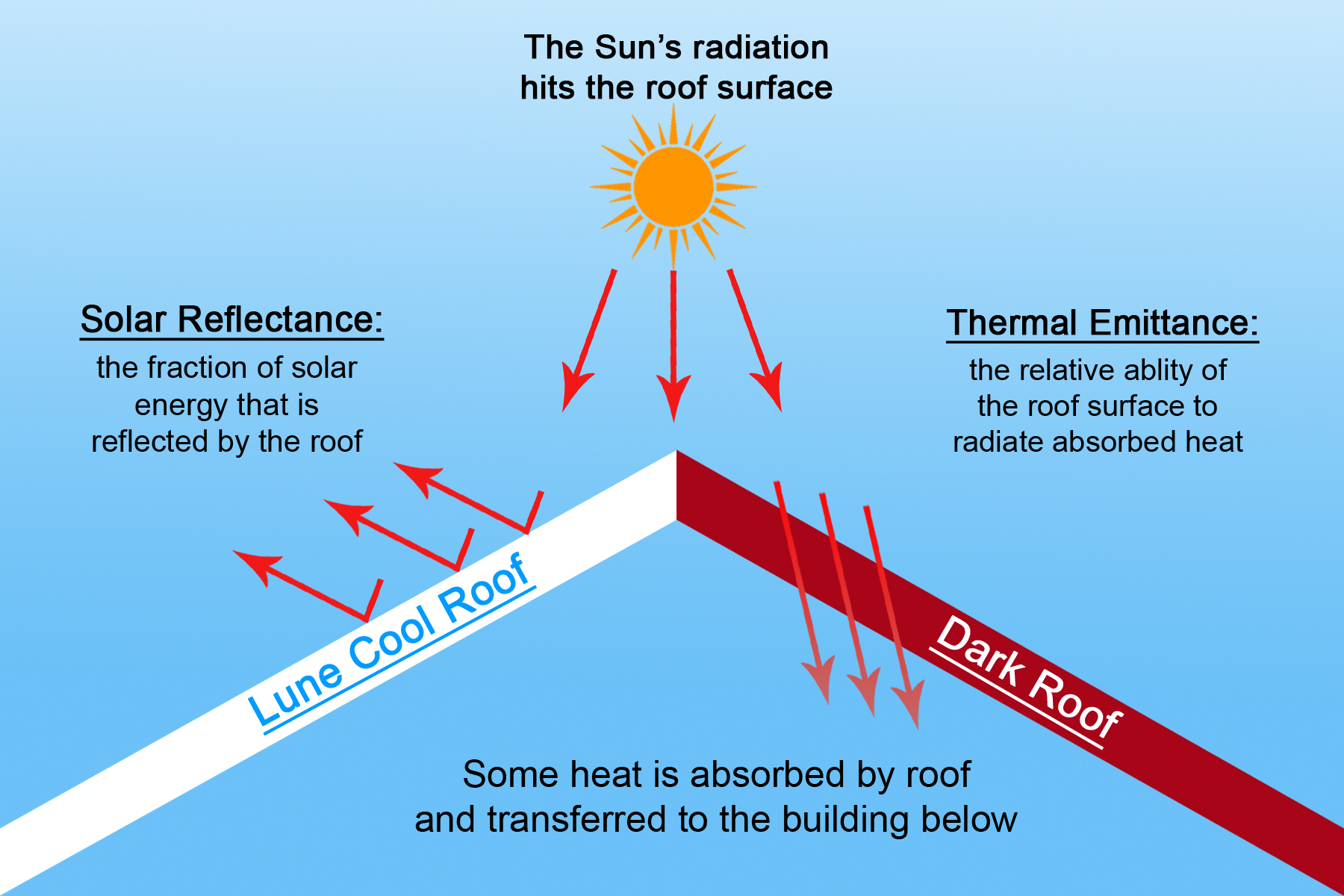
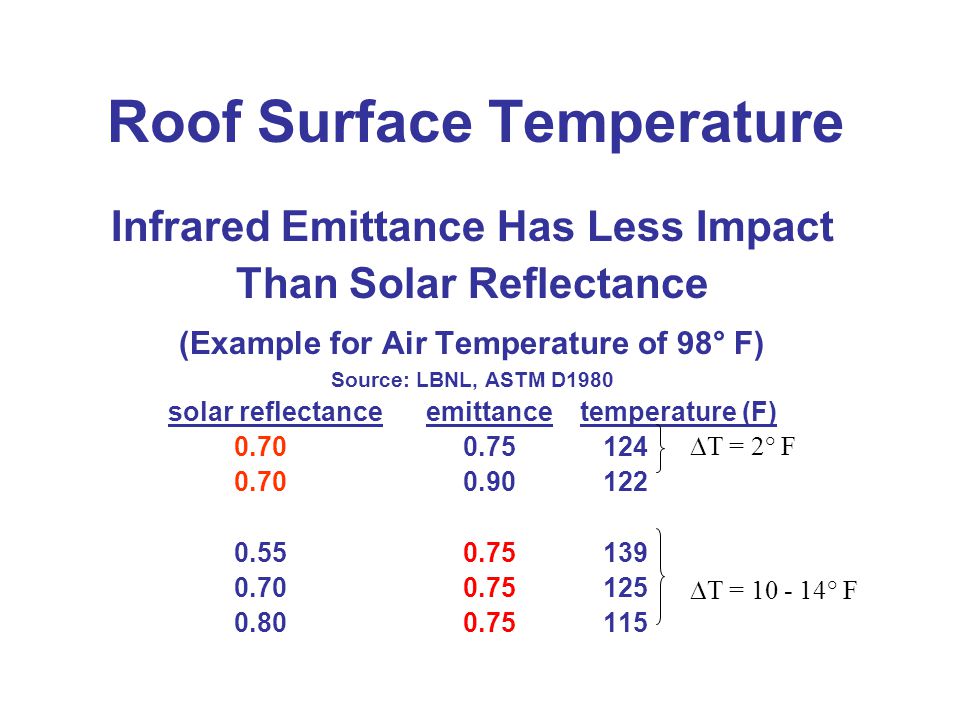
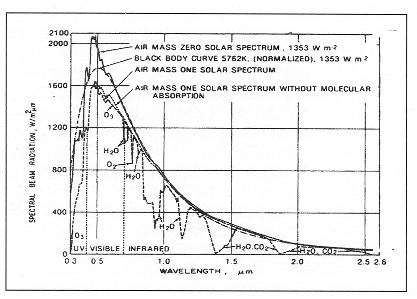
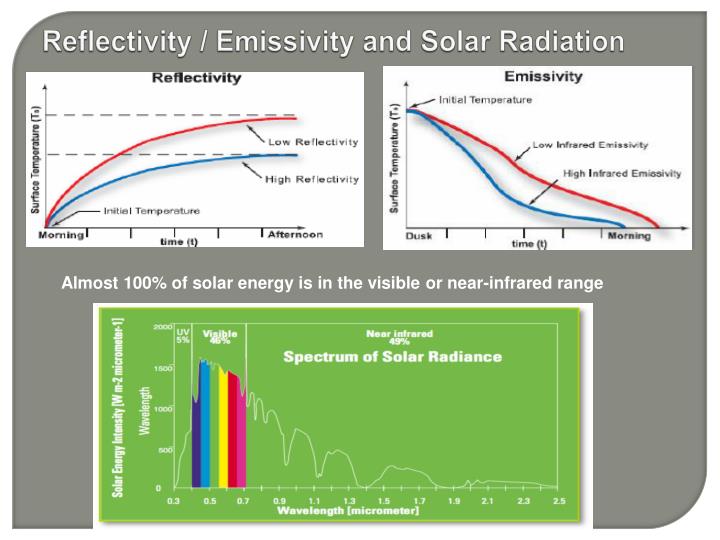
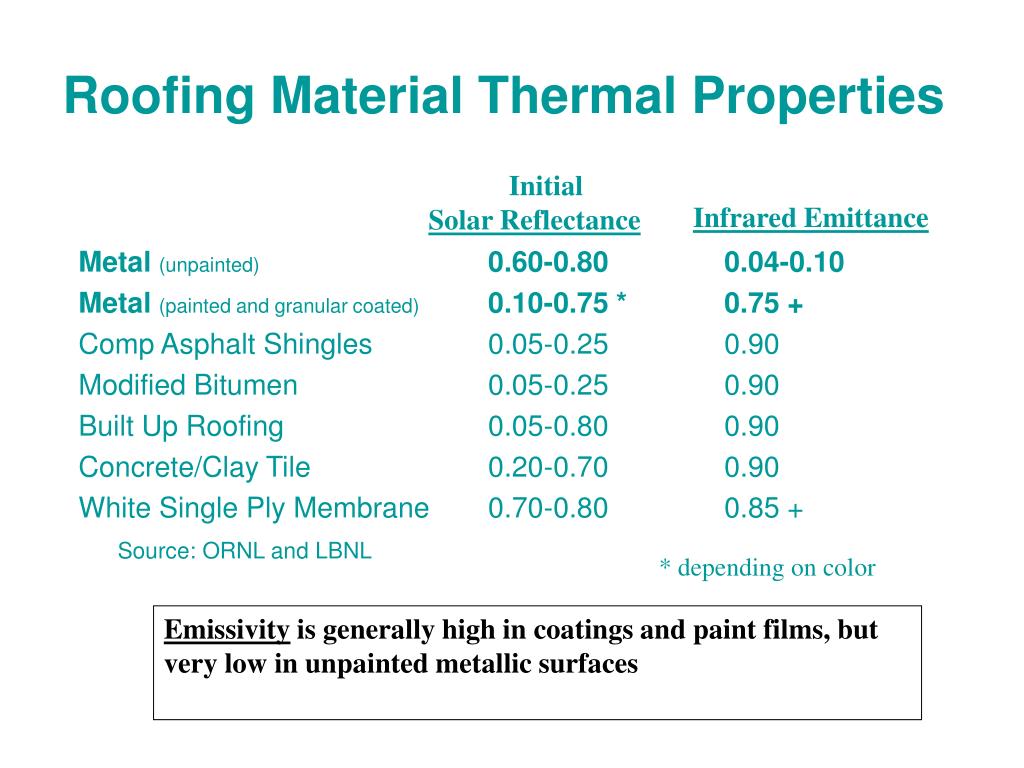
Ir emittance roof. For building products thermal emittance measurements are taken for wavelengths in the infrared. However emittance also matters because the higher the emittance the more readily the roof surface will radiate long wave ir heat to the sky. The term solar reflectance is a measure of the amount of that solar energy that is immediately reflected from the surface. Just like reflectance the emittance of the roof is measured on a scale of 0 to 1 with 1 being the highest.
A cool roof on nonresidential buildings is defined as one with a 3 year aged solar reflectance of at least 0 55 and an infrared emittance of at least 0 75 or minimum sri of 64 in climate zones 2 through 15 for low slopes 2 12 or less. Applied them to stone coated metal shakes thermal performance of the stone coated metal roofs. In common construction applications the thermal emittance of a surface is usually higher than 0 8 0 85 except for those layers that are based on metallic components for example aluminum shingles. In today s market a cool roof is defined by the reflectivity and emissivity requirements set by either title 24 from the california energy commission or by the energy star program.
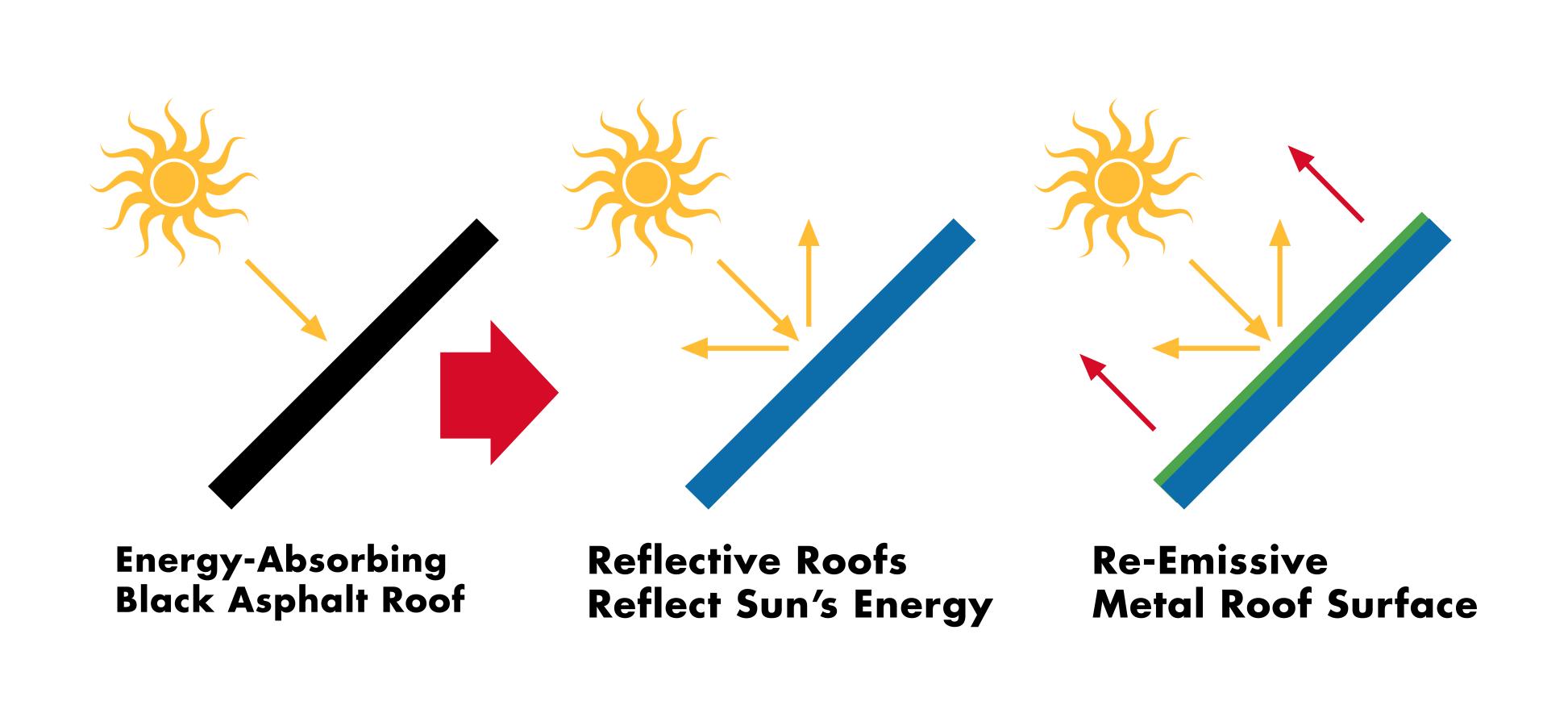
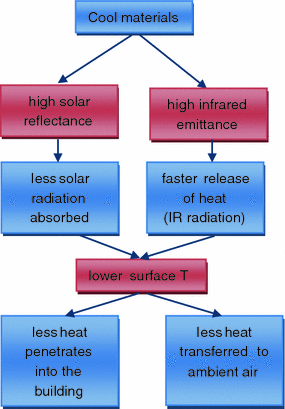
Cool roofs achieve this by reflecting some of the infrared ir light from the sun. As such it plays an equal if not greater role in defining what s a truly energy efficient roof. Solar reflectance and thermal emittance are the two key material surface properties that determine a roof s temperature and they each range on a scale from 0 to 1. Link between energy savings and emissivity.
One example is a metal wrench left in the sun which is hot to the touch because it has a low emissivity value. In general a cool roof is one that has relatively high solar reflectance and high thermal emittance. They can also reduce the urban heat island effect. The larger these two values are the cooler the roof will remain in the sun.
During the daylight hours a roof is constantly subjected to solar energy striking its surface. The thermal emittance of a roof or wall component is mainly affected by the characteristics of the layer that is exposed to the solar radiation. Scientists use a number between 0 and 1 or 0 and 100 to express emittance. With the exception of a metallic surface most roofing materials can have emittance values above 0 85 85.
A low thermal emittance provides improved get content here.